
Mar 19, 2021
Democracy is under siege around the world with the subversion of democratic processes and outright coups—and attacks worker rights are a big part of authoritarian efforts to cut off civil liberties.
On this week’s Solidarity Center Podcast, two worker advocates from countries where democracy is under threat—Belarus and Brazil—discuss how workers are pushing back against repression and are building a better future for their countries, one that recognizes worker rights are a foundation of true democracy.
Maximilano Garcez, president of the Brazilian Association of Union Lawyers, represented families of the 272 people who died in a preventable mining disaster in 2019. The Brumadinho mining waste dam, held by walls of sand, collapsed during rainy season cutting a path of destruction from the mine and for miles into the surrounding community. It is among nearly 100 mining dams in the country built the same way.
The mining disaster was “industrial homicide”—the result of corporations “incentivized to greed” in a system where “killing people has been worthwhile,” says Garcez.
Workers Rise Up in Belarus Against Repressive Regime
Also on the show, Sergey Antusevich, vice president of the Belarusian Congress of Democratic Trade Unions, describes the recent uprising against the country’s repressive regime in which workers, led in many cases by women, have taken a key role.
“Many factories began to express a position actively, protest against violence and fraud, and started for the first time in Belarus history to set up strike committees” despite a strike ban, he says.
“At the same time, the protesters made demands: resignation of Lukashenko and his clique and an end to violence and repression and holding fair elections. At the same time, workers and employers began to quit the state trade unions and tried to create independent trade unions.”
The Solidarity Center Podcast, “Billions of Us, One Just Future,” highlights conversations with workers (and other smart people) worldwide shaping the workplace for the better.
Join us for a new episode each Wednesday at iTunes, Spotify, Amazon, Stitcher or wherever you listen to your podcasts.
Solidarity Center Podcast Schedule
- March 24: Preeda, a migrant worker rights activist in Thailand working with unions to help migrant workers meet the challenges of COVID-19.
- April 7: Francia Blanco, a domestic worker and trans rights activist reaching marginalized workers through her all-trans domestic workers union.
- April 14: Adriana Paz, an advocate with the International Domestic Workers Federation who understands firsthand the power of unions in ensuring domestic workers have safe, decent jobs.
- April 21: International Trade Union Confederation President Ayuba Wabba, who explores the Nigerian labor movement’s response to the COVID crisis on workers and discusses the global labor movement’s plans to build back better for workers around the world.
This podcast was made possible by the generous support of the American people through the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) under Cooperative Agreement No.AID-OAA-L-16-00001 and the opinions expressed herein are those of the participant(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of USAID/USG.

Mar 17, 2021
The COVID-19 pandemic has hit workers hard—but women have especially suffered compared with men, experiencing higher rates of unemployment, discrimination and exposure to the virus, and skyrocketing rates of gender-based violence and harassment (GBVH), speakers said this week at a Solidarity Center panel. Unions are organizing to demand that government responses to the pandemic’s economic and social effects center on the needs and experiences of women workers, ensuring safety and respect for all workers.

“Women have suffered because most of the work they do is precarious”—Rose Omamo, Kenya
“Women have suffered because most of the work they do is precarious—they are informal workers, frontline workers,” said Rose Omamo, general secretary of the Amalgamated Union of Kenya Metalworkers. Omamo explained how COVID-19 has shown the need to extend social protections like paid sick leave and health care to all workers, and to address issues affecting women in Kenya and worldwide. She shared that rape and sexual assault in the world of work has increased because of economic stress caused by the pandemic, including an increase in domestic violence and increased demands for sexual favors in order to obtain or keep a job. Kenyan unions are organizing to demand that social protections include access to reproductive health services in light of increased sexual violence, and are bargaining with employers to increase protections against GBVH in the workplace.
Omamo was among five women union leaders and Solidarity Center partners who took part in “Women Workers’ Voices and Participation on the COVID-19 Recovery Front Lines,” a virtual parallel event during the United Nations Commission on the Status of Women (CSW) as part of the NGO CSW65 Virtual Forum.
Employers, Government Failing Women Workers in the Pandemic

Employers have used COVID-19 as an excuse to violate worker rights, says Cambodian union leader Ou Tepphallin.
Employers have taken advantage of the pandemic to exploit, abuse and lay off workers, panelists said. “Labor rights have been violated during COVID-19 as employers used the opportunity to exploit the system,” said Ou Tepphallin, president of the Cambodian Food and Service Workers Federation.
Retail, hospitality and garment workers in Cambodia, the majority of whom are women, have not been provided adequate personal protective equipment (PPE) or measures to ensure their safety, and unscrupulous employers have taken advantage of the crisis to exploit and abuse workers. For example, workers in the hospitality sector report that entertainment venues have opened illegally during lockdown and forced workers to return to work. Some companies deliberately targeted older or less conventionally attractive workers for layoffs. Unions have been organizing to hold employers to account, negotiating for better protection measures, including protections from GBVH.

When women are in unions, they can speak out against mistreatment and come together to create solutions, says Honduran union leader Iris Munguia.
In Honduras, the impact of the pandemic collided with ecological and social crises. The devastation caused by two hurricanes in November 2020 left many women homeless and struggling to support their families, said Iris Munguía, women’s coordinator of the Honduran Federation of Agro-industrial Unions (FESTAGRO). In addition, women experience extremely high rates of GBVH, which is treated with impunity in Honduras. More than 30 women have been murdered in 2021, and “there are no investigations of these murders,” Munguia said.
The combined crises have left women workers more vulnerable than ever to exploitation and abuse. The majority of workers laid off during the pandemic were women, and unions have been organizing to ensure women workers are at the bargaining table to win protections from employers, including access to childcare, adequate protective equipment and protections against GBVH at work. Unions in the agricultural sector are demanding that multinational companies do more to ensure greater safety on the job. Munguia discussed the power of union organizing, stressing that women in trade unions had the ability to speak out against mistreatment and come together to create solutions.
In Honduras, Munguía is part of a campaign for C190 ratification, while also training women to be part of negotiations with employers so they can advocate for contract clauses that benefit them, such as childcare and a violence-free workplace.
“We have a great advantage by being unionized,” she said. “Whenever we face discrimination, harassment, we can report it, denounce it, talk about it—and that opportunity is there because we are part of a union.”
‘We Have a Great Advantage: We Are in a Union’

UGTT’s Nadia Bergaoui shared images of women agricultural workers as she discussed the challenges they face at work.
In the face of such challenges, women have stepped up their efforts to achieve justice at the workplace, according to the panelists, including efforts to push their governments to ratify Convention 190. Adopted by the International Labor Organization in 2019, the convention seeks to end violence and harassment in the world of work, including gender-based violence.
Across Tunisia, where 500,000 women work in the informal agricultural sector, the Federation of Agriculture and the Tunisian General Labor Union (UGTT) are working to end gender-based violence through awareness-raising programs that ensure women know their rights on the job and can speak out for safe conditions, especially on the dangerous transport to and from work, said Nadia Bergaoui.
Bergaoui, general secretary, media officer and women’s affairs officer of the Federation of Agriculture, said a union survey in 2020 found that more than half of women said they have faced verbal or physical abuse on the job, and lack access to paid time off, sick leave or health care. The union is organizing workers to demand safe transportation, protections against GBVH, PPE and access to social protections.
Unions in Kyrgyzstan are advocating for protections for women workers, says Gulnara Derbisheva.
Gulnara Derbisheva, director of Insan Leilek, discussed how unions in Kyrgyzstan are advocating for protections for women workers, including demanding that the government address the increase in GBVH during the pandemic by ratifying Convention 190. Unions, with Solidarity Center support, opened a women migrant worker center in Bishkek, where workers have reported increases in GBVH and other abuse on the job. She shared how she is working with unions to advocate for greater protections for women migrant workers, including ratification of C190.
“Unless we keep advocating, we will be in a standstill,” she said.
Watch a recording of the event, simultaneously translated for Arabic, English, Khmer, Russian and Spanish speakers.

Mar 10, 2021
“Violence and harassment happens to all workers, irrespective of your gender,” says Brenda Modise, a union activist in South Africa. “It doesn’t matter whether they are men and women, old young LGBTQI community or anyone, but we are addressing violence and harassment in the world of work against all workers.”
Modise spoke with Solidarity Center Executive Director Shawna Bader-Blau in first episode of The Solidarity Center Podcast, “Billions of Us, One Just Future,” which highlights conversations with workers (and other smart people) worldwide shaping the workplace for the better.
(Join us for a new episode each Wednesday at iTunes, Spotify, Amazon, Stitcher or wherever you listen to your podcasts. )
Front-line Leaders Building a Future Inclusive of All Workers
 The Solidarity Center Podcast’s seven-episode season will feature worker advocates from around the world:
The Solidarity Center Podcast’s seven-episode season will feature worker advocates from around the world:
- Maximiliano Garcez, a labor rights lawyer who describes workers’ efforts to seek justice following a deadly mining accident in Brazil.
- Adriana Paz, an advocate with the International Domestic Workers Federation who understands firsthand the power of unions in ensuring domestic workers have safe, decent jobs.
- International Trade Union Confederation President Ayuba Wabba, who explores the Nigerian labor movement’s response to the COVID crisis on workers, and discusses the global labor movement’s plans to build back better for workers around the world.
- Preeda, a migrant worker rights activist in Thailand working with unions to help migrant workers meet the challenges of COVID-19.
- Sergey Antusevich, a brave union leader in Belarus working for democratic freedom in a repressive regime.
- Francia Blanco, a domestic worker and trans rights activist reaching marginalized workers through her all-trans domestic workers union.
These front-line leaders will share the steps they are taking to shape their livelihoods at the workplace and in their communities in the face of escalating attacks on democracy and civil rights, and explore how they seek to build a more equitable future, one inclusive of all workers as the COVID-19 pandemic upends structures, systems and societies.
‘Tears of Joy’

Union activists celebrate after the ILO adopts Convention 190 to end gender-based violence at work. Credit: ITUC
In the first episode, Modise shares how she and women unionists around the world campaigned for adoption of an International Labor Organization convention (regulation) on ending gender-based violence and harassment in the world of work, and how they are moving forward the campaign by pushing their governments to ratify Convention 190.
“We need to put more effort as the women in South Africa to make sure that whatever that you have were fought for is going to be realized in South Africa and be incorporated into our own legislation and make sure that it is implemented. We should not only have beautiful legislation, but we should have implementable legislation that we can be able to monitor and evaluate.”
As Modise heard an audio clip of women unionists singing and clapping the moment Convention 190 was adopted in 2019, she reflected on her experience.
“It was a breathtaking moment. We all shed tears. It was tears of joy because remember, when you went into that room as workers of the world, we knew what we wanted, but we didn’t know if the business constituents of the world understand where we are coming from.
“It really feels great, even though the bigger work has not yet started. We really want South Africa to ratify the convention. The work is not going to be ending at ratification. It’s also going to go in terms of after ratification, what next, and that’s where the bigger role and our activism is going to be needed.”
This podcast was made possible by the generous support of the American people through the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) under Cooperative Agreement No.AID-OAA-L-16-00001 and the opinions expressed herein are those of the participant(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of USAID/USG.

Feb 4, 2021
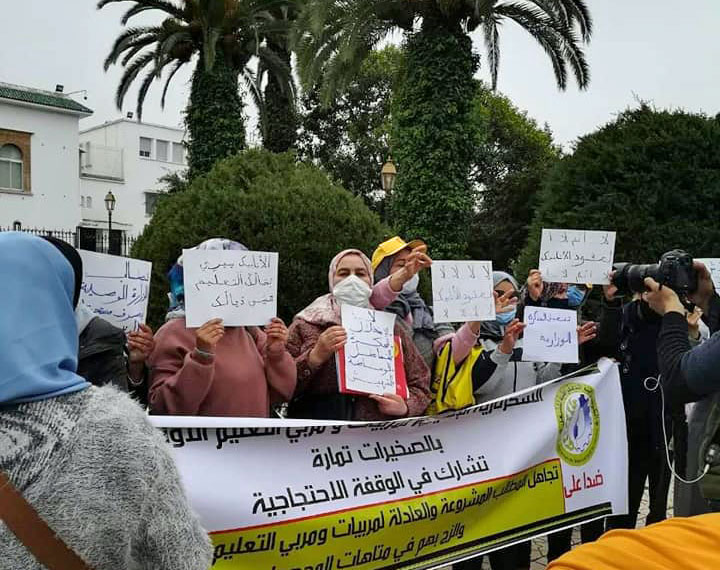
Teachers carried out protests throughout January against a government crackdown on their fundamental freedom to strike, with rallies at the Ministry of National Education and Vocational Training in the capital, Rabat, and across the country. Teachers also are protesting the working conditions of contractual teachers and the Ministry of Education’s refusal to engage in social dialogue.

The CDT is calling for nationwide protests February 10 around education worker demands. Credit: CDT
Morocco’s constitution has protected the right to strike since 1962, but the government seeks to revise the country’s labor law by adding significant obstacles to the right to strike, in violation of Morocco’s international legal obligations. Unions are calling on the government to engage in real social dialogue to develop legislation consistent with international law.
“These abusive measures constitute a flagrant violation of the constitution, of the guarantee of the right to strike and of national laws, as well as against international conventions that consider the right to strike a fundamental part of freedom of association,” the Democratic Labor Confederation (CDT) wrote in a December letter to Educational International. The global federation, Education International, strongly supports the CDT and the National Union of Teachers (SNE) in their efforts to push back against the government’s moves to limit essential worker rights.
The government also barred a planned December 22 sit-in on at the Education Ministry headquarters in Rabat, citing exceptional circumstances and the law on health emergencies. Union members and leaders called the ban illegal and said security service used force to disperse them before they could reach the Ministry’s headquarters.
The January actions follow a series of rallies and sit-ins across Morocco last fall, including a national general strike on December 1 and 2, as teachers protested the government’s move to reduce their seniority and promotion opportunities and its replacement of full-time teachers with teachers on contract who are paid lower wages and have no job security.
Education Officials Refuse to Meet with Teachers
Morocco’s workers and their unions have been left out of discussions regarding management of the COVID-19 crisis and educational continuity, according to the SNE-CDT. The union says the ministry has not fully addressed health and safety conditions for teachers, education support staff and pupils.
Education ministry officials have frozen dialogue with teachers, last meeting with them in February 2019. One of the union’s fundamental demands is for the government “to open a serious and responsible dialogue on the outstanding demands from 2014 to today, and the respect of trade union freedoms and the right to strike.” Among the unresolved issues are improved wages, a voice for teachers in the education reform process, investment in public education, teacher training and more staffing to lower classroom size.
In early January, the CDT also spoke out against the ministry’s unilateral decision to cancel upcoming examinations for middle and high school students due to the pandemic, highlighting another example of how the education ministry fails to involve the representatives of teachers and other employees of the public school system in decision making.
More Teachers on Contract, with Few Rights
In early 2019, a government decree removed the option of workers with renewable two-year employment contracts to integrate into the public sector, a move that means contract teachers have no access to fair wages and social benefits like pensions, health care or job security. The CDT has sought to replace fixed-term contracts with permanent employment.
The number of fixed-term teaching contracts is increasing in Morocco and undermines the core notion of public service. The change grants the government a waiver on its obligations, according to a recent CDT field study on the future of work in the education sector, carried out in collaboration with the Solidarity Center. “Some of the direct results of casualization, as identified through the study, include instability, precariousness, dissatisfaction and lack of confidence in the profession’s future,” the CDT notes.
The study also finds an increasing number of women in all levels of the education system, and the future of work in the education sector must address this shift, says Younes Firachin, a member of the National Office of the National Education Union. That requires unions “to fully grasp these transformations” to effectively reach them and address their concerns, he says.
Employees throughout the public education system, frustrated by the lack of attention to their terms and conditions of employment, increasingly are joining the protests. On January 27, many who provide assistance to young children in kindergarten and primary school rallied in Rabat.
The CDT also announced a series of nationwide protests set for February 10 to mobilize administrative and technical assistants to call for their recognition by the Ministry of Education and Morocco’s public school system.

Sep 9, 2020
The Tunisian General Labor Union (UGTT) is calling on employers and the government to join with it in addressing the severe challenges textile workers are facing during the COVID-19 crisis and negotiate an action plan to guide the struggling garment sector.
Some 160,000 workers, the vast majority of whom are women younger than age 35, work in Tunisia’s textile industry, which accounts for 34 percent of the country’s manufacturing sector. Following the country’s coronavirus lockdown, workers lost jobs and pay, in part because the industry experienced a 45.2 percent decline in textile exports in March from the previous year, according to the National Institute of Statistics in Tunisia. Many corporate brands also canceled “mid-season” orders.
But crucially, employers also took advantage of the COVID-19 crisis to cease or suspended paying workers’ social security benefits or family allowances, such as food tickets, under the pretext of force majeure, union leaders say. Employers coerced workers, especially new employees, into signing fixed-term contracts and giving up their status as permanent workers. Workers also say some employers blocked their efforts to form unions to gain fundamental rights on the job, closed union offices—prohibiting workers from meeting in the office even outside working hours—and removed posters and other legally placed union material from worksites.

Habib Al-Hazami. Credit: General Federation of Textile Leather and Footwear
“All trade union activists and the General Federation affirm that the garment and textile sector in Tunisia has been marginalized and is facing a crisis,” says Habib Al-Hazami, general secretary of the General Federation of Textile, Leather, and Footwear.
In April, the Tunisian General Labor Union (UGTT) and the Tunisian Federation for Industry and Trade entered into a landmark agreement on workers’ wages, including textile workers’ wages. The government agreed to contribute $73 per worker, with the remaining salary paid by employer. Employers also agreed to register unregistered workers with the National Social Security Fund within a month after the agreement to ensure they are eligible for social benefits.
Although the lockdown ended June 27 and many factories resumed nearly full production, union leaders say worker rights’ violations persist, with factories not following government regulations to slow the spread of the novel coronavirus.
In calling for discussions with employers and the government, UGTT is seeking to:
- Strengthen job security for garment and textile workers by reducing short-term contracts and increasing formal employment.
- Examine how best to restructure the sector with a focus on ethical market competition so workers do not bear the brunt of corporate brands’ rush for products at the lowest cost.
- Take urgent steps to end gender-based violence and harassment at work and ensure decent working conditions.
- Increase workplace inspections to monitor potential safety and health violations.
- Create space for workers to form and join unions so they have a voice on the job.









 The Solidarity Center Podcast’s seven-episode season will feature worker advocates from around the world:
The Solidarity Center Podcast’s seven-episode season will feature worker advocates from around the world:



