
Jun 16, 2021
Jesmin Begum, a Bangladesh garment worker in her early 30s, died as she and hundreds of others rallied for unpaid wages in one of Dhaka’s Export Processing Zones (EPZs).
A sewing operator, Begum was laid off in January from Lenny Fashion, Ltd., after the factory closed. Although management said it would pay unpaid wages by May, the company never fulfilled its commitment, and workers gathered at the Nabinagar-Chandra highway outside the EPZ June 13 to demand payment.
When the workers at Lenny Fashion Ltd. and another factory that was closed by the same company refused to move from the road after two hours, the police used tear gas, rubber bullets and water cannons to disperse them, and Begum died after she fell fleeing the police violence. Dozens of workers also were injured.
“We are always told that in EPZ factories, BEPZA [Bangladesh Export Processing Zones Authority] enforces workers’ rights properly and vigorously, but BEPZA, as in many other previous cases, has miserably failed here that led to the workers’ protest and death of Jesmin,” says Babul Akhter, president of the Bangladesh Garment and Industrial Workers’ Federation (BGIWF)
Worker Rights Abused, EPZs Make Billions
Bangladesh’s eight EPZs received $333.38 million in foreign direct investment and made $7.52 billion from exports in the 2018–2019 fiscal year. Yet Bangladesh workers in EPZs face daunting odds in trying to redress often poor and dangerous factory safety and health conditions, retrieve unpaid wages or end abusive treatment by supervisors because the zones are exempt from the country’s labor laws and workers are prohibited from forming unions.
As a result, they are particularly vulnerable to worker rights abuses. Although they are allowed to organize and form workers welfare associations (WWAs) at their factories, the WWAs do not have the same rights as unions. The ILO Committee of Experts has identified numerous provisions in the WWAs that violate ILO Conventions 87 and 98 on the freedom to form unions an bargain collectively.
The terms and conditions of service for EPZ workers are regulated by BEPZA, essentially eliminating collective bargaining. Labor inspectors are not permitted to inspect factories in the zones and, unlike workers covered under the nation’s labor laws, workers in EPZs do not have the legal right to file a case challenging illegal termination.
In addition, says Akhter, “BEPZA and the employers are systematically dissolving the worker welfare associations in EPZ factories to eliminate any kind of voice of the workers in the workplace.”
With Unions, Workers Advocate for Safe Jobs
Although the government of Bangladesh in 2019 amended the EPZ law with the aim of bringing it more in line with its labor laws and international labor standards, the ILO found the new EPZ Law failed to address the vast majority of these concerns. “Importantly, the new law continues to deny EPZ workers the right to form or join a union,” according to the ILO.
“The EPZ workers must be allowed to exercise their rights to join union of their own choosing, removing the discrimination between the EPZ and non-EPZ workers,” Akhter says.
Without the ability to form unions, garment workers cannot collectively push for safety and health improvements at their workplaces. After more than 1,200 garment workers died in two tragic factory disasters in 2012 and 2013, unions have been a key partner with fashion brands in the Accord on Fire and Building Safety in Bangladesh, a landmark agreement that made factories safer for 2 million garment workers. Worker rights advocates are urging extension of the Accord, which expires in three months.
Yet the BEPZA did not allow the Accord to inspect any of the EPZ factories—all the more reason, worker advocates say, garment workers must be able to form union and collectively bargain.

Jun 15, 2021
On June 16 International Domestic Workers Day, domestic workers are celebrating a landmark legal win by South Africa’s domestic workers for colleagues who die or are injured in their employers’ homes. For the first time, starting this year, domestic workers who suffer injury on the job are eligible for compensation for temporary and permanent disability, medical expenses, funeral costs and survivor benefits.
Until last year, South Africa’s approximately 1 million privately employed domestic workers suffered deaths and crippling injuries without access to compensation for themselves or their dependents because domestic workers were excluded from South Africa’s Compensation for Occupational Injury and Illness Act (COIDA). With Solidarity Center support, the South African Domestic Service and Allied Workers Union (SADSAWU) and human rights organization Socio-Economic Rights Institute of South Africa (SERI) litigated and won a long-denied claim for the dependent daughter of Maria Mahlangu, a privately employed and partially sighted domestic worker who had fallen into her employer’s swimming pool and drowned in 2012. The historic judgment, made by the South African Constitutional Court in mid-November, recognized that injury and illness arising from work as a domestic worker in a private home is no different to that occurring in other workplaces and thus equally deserving of COIDA coverage.
Myrtle Witbooi, general secretary of SADSAWU and the first president of the International Domestic Workers Federation (IDWF), said in addition to the last year’s court ruling, South Africa’s domestic workers can also celebrate this year’s hard-fought win under revised compensation rules of three years of retroactivity to submit claims.
Under the new rules, all employers of domestic workers must register with the Compensation Fund or face penalties, and make annual payments to cover their employees. SADSAWU is focusing its efforts on educating employers and domestic workers about their obligations and rights under the new rules, says Witbooi. SERI made a new domestic worker compensation information fact sheet available to domestic workers, paralegals and community advice offices this month, while SADSAWU is producing and distributing an educational WhatsApp video and pamphlet and translating the amendment into local languages.
The unions and SERI continue to press the government for more time for domestic workers to submit claims and increase retroactivity. “We must remain that beacon of hope for workers,” says Witbooi.
Meanwhile, another domestic worker, Nobuhle Ndlovu, drowned in her employer’s swimming pool last month.
Ten years after the adoption of an International Labor Organization (ILO) Convention confirmed their labor rights, domestic workers across the globe are still fighting for recognition as workers and essential service providers, as documented by a new ILO report. And, although 32 countries have ratified Domestic Workers Convention 189, and 29 have entered the convention into force, most of the world’s 75.6 million domestic workers are still being denied social protection rights, including access to national health insurance, pension schemes and compensation funds.

Jun 8, 2021
Worker rights and human rights advocates are urging multinational corporate fashion brands to commit to a binding successor agreement that will continue the pathbreaking work of the Accord on Fire and Building Safety in Bangladesh, a landmark agreement that made factories safer for 2 million garment workers.
Signed by fashion brands and unions in 2013, the Accord was set apart from previous safety agreements because it was legally binding, providing a key enforcement mechanism for workers and their unions to hold individual brands and retailers accountable. As a result, the Accord “has been the most successful safety program in the contemporary history of apparel supply chains,” according to a recent report by a coalition of worker rights organizations.
It was set to expire May 31, but corporate brands agreed to a three-month extension to allow for more time to conclude negotiations on a new binding safety agreement.
Accord Boosted Safety for Millions of Workers
The Accord “actively engaged with unions to ensure that workers voices are heard in the remediation process to ensure safety in the workplace,” says Rashadul Alam Raju, general secretary of the Bangladesh Independent Garment Union Federation (BIGUF).
“In five years, thousands of fire, building and electrical hazards were fixed in the [ready-made-garment] RMG factories,” he says. “As a result, safety standards were uplifted for millions of workers [and] the country has not witnessed any major accidents or loss of life in the factories inspected by Accord.”
The Accord, which now includes more than 190 brands and covers 1,600 factories, was signed after more than 1,100 garment workers were killed in the April 2013 Rana Plaza collapse in Bangladesh. Voluntary programs, with no legally binding enforcement like the Accord, failed to prevent the Rana Plaza collapse or the tragic Tazreen Factory fire that killed more than 100 Bangladeshi garment workers a few months earlier.
Accord Ensured Workers, Their Unions a Voice

BIGUF General Secretary Rashadul Alam Raju says the Accord ensured safety for millions of workers and must be extended. Courtesy Rashadul Alam Raju
Following a 2020 Bangladesh High Court decision, the Accord’s day-to-day operations were handed over to the Ready-Made Garment Sustainability Council (RSC), comprised of brands, factory owners and global and local unions. But the RSC is not legally binding and, “for all intent and purposes, is not going to bring about any real change in the factory conditions,” says Raju.
Crucially, the Accord supported an environment in which workers’ voices could be heard through collective bargaining between unions and employers, enabling unions to protect workers’ safety and ensuring they woud not be targeted by managers for speaking out about their workplace rights.
“The Accord was very much proactive in engaging with the unions in its work to ensure safety for the workers,” says Raju. “This also ensured protection to the workers and unions from being victimized by the employers. But such protection with RSC is virtually non-existent.”
Bangladesh garment workers, primarily women who often are subject to brutal verbal and even physical violence for supporting unionization, were able to form dozens of unions in the wake of the Accord, with tens of thousands achieving first-ever rights on the job.
Raju and other Bangladesh union leaders say the Accord’s signatory brands must agree to a new binding safety agreement that ensures safe work, remains individually enforceable upon brands, keeps an independent secretariat in place that oversees the brands’ compliance and allows for expansion to other countries.
Although brands committed in January 2020 to negotiate a new binding agreement with the option to expand to other countries, they since have offered only a watered-down version of the Accord.
A renewed agreement is urgently needed, union leaders say, because much work still must be done to ensure factory safety in Bangladesh and around the world. A renewed agreement offers the possibility of expanding factory safety and health to other countries, where recent disasters underscore the need to address life-threatening work environments.
The bottom line, says Raju, is that unions must be part of any new agreement, “but it has to be legally enforceable.”

Jun 2, 2021
A police crackdown against Lesotho garment workers protesting a two-year delay in scheduled minimum wage increases resulted in two fatalities in Maseru, the capital, last week. Pitso Mothala and Motselisi Ramasa died as police fired into the crowd. Many more workers were injured.
The deaths come after two weeks of escalating state-sponsored attempts to use shootings, beatings and arrests to force thousands of the country’s 50,000 garment workers to return to their factories. Meanwhile, government ministries have rejected union attempts to negotiate an end to protests and are still refusing to provide garment workers with the wage increases they need to sustain themselves and their families through the COVID-19 pandemic, reports United Textile Employees (UNITE).
“We want justice for our brutal[ally] killed comrades and we shall forever make sure that their blood is not in vain,” says a UNITE media release that identifies the two slain garment workers by name. Garment workers remain at home this week while the country’s armed forces continue to patrol the industry, reports the union.
The country’s unions are refusing to return to work until the government makes good on two missed incremental minimum wage increases—for 2020/2021 and 2021/2022—that have been delayed indefinitely.
Lesotho has a long history of human rights violations against political and labor activists, including police violence against peacefully striking factory workers rallying for fair wages last year. The 45th annual U.S. Department of State, Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor Human Rights report on Lesotho found that members of the Lesotho Mounted Police Service and Lesotho Defense Force last year committed numerous human rights abuses, including “unlawful or arbitrary killings; torture and cases of cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment or punishment; harsh and life-threatening prison conditions [and] arbitrary arrest or detention.”

Jun 1, 2021
Half or more workers in key Cambodian industries were suspended for three or four months, and most were unable to support themselves on government aid during the pandemic, according to a new study that put hard data to the suffering of the country’s low-wage workers.
Some 53 percent of those working in tourism were suspended for an average 15 weeks, and 40 percent of workers in Cambodia’s garment and footwear industries were suspended for an average of 11 weeks, according to a survey of 1,525 workers by the Center for Policy Studies. Solidarity Center and The Asia Foundation supported the research, which reports results from July and August 2020. (See the full survey.)
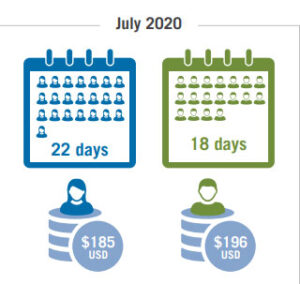
Women workers in Cambodia worked more and were still paid less than men during the pandemic. Source: CPS/Solidarity Center/Ponlok Chomnes
Women comprise the majority of workers surveyed and are the majority of 800,000 workers in the country’s garment and footwear industries. Before the pandemic, women were typically paid less than men. Yet, even when they returned to work in July 2020, they reported being paid less than men even though they worked more days than men.
All workers who returned to the job by July 2020 on average were employed for fewer hours and earned less than in July 2019.
COVID-19 an Excuse to Exploit Workers
Although many businesses were forced to temporarily suspend operations or shutter permanently during Cambodia’s first wave of COVID-19, some employers took advantage of the pandemic to lay off workers, union leaders say.
Further, hospitality and garment workers who returned to, or remained on the job, were not provided adequate personal protective equipment (PPE) or measures to ensure their safety, according to union leaders in Cambodia. Unions have been organizing to hold employers to account, negotiating for better protection measures.
Government Support Helpful, Not Sufficient
To assist garment and tourism workers during the country’s first wave of COVID-19, the Cambodian government launched several programs, including financial support for workers suspended from the job and a skills improvement training program. But workers interviewed for the survey said the suspension payments, which ranged $40 to $70 per month, were not sufficient to cover the roughly $69 they needed for basic monthly food expenditures.
Half of those surveyed say the suspension allowance was their only income, and more than 50 percent said they could not afford to send remittances to their family as a result of pandemic-related losses. Between 40 percent and 60 percent of workers surveyed say they took on debt to survive.
The government announced in July 2020 that businesses closed during COVID-19 were not required to pay workers hardship or layoff wages. Tourism sector operations also were not required to contribute the $30 per month toward the suspension payments. The government provided $40 per month.
Urgent Action Needed for New Pandemic Wave
Since February, Cambodia has experienced its worst COVID-19 outbreak, which has led to a deepening crisis for workers as many major cities and several provinces have been in strict lockdown.
During the pandemic, workers in many industries have been left out of public social protection programs, such as health coverage, and the survey recommends extension of these benefits for the most vulnerable.
The survey also recommends expanding skills improvement training programs and funding opportunities for temporary jobs.
Without such support, garment workers like Eang Malea are returning to their factories despite the risk of contracting COVID-19.
“I need to pay rent, utilities and debts, ” Malea, 26, said. “I worry that I will get infected by going to work without being vaccinated, but I don’t really have a choice.”







