Apr 8, 2014
 The governments of Colombia and the United States signed the Labor Action Plan (LAP) three years ago this week. The plan was intended to provide a road map for Colombia to protect internationally recognized labor rights, prevent violence against labor leaders and prosecute the perpetrators of such violence.
The governments of Colombia and the United States signed the Labor Action Plan (LAP) three years ago this week. The plan was intended to provide a road map for Colombia to protect internationally recognized labor rights, prevent violence against labor leaders and prosecute the perpetrators of such violence.
As a new AFL-CIO report shows, systemic violence against Colombian workers continues and workers still face persistent employer abuses. Palm workers like Miguel Conde of the union SINTRAINAGRO at the Bucarelia plantation initially were hopeful, but the LAP profoundly failed to deliver on its promises. In the blog, “Make the Colombia Labor Rights Action Plan Work for Workers,” the AFL-CIO Now writes:
“Like many Colombian workers, palm workers at Bucarelia were increasingly hired on as temporary subcontracts. Subcontracting prevents workers from forming unions, gets employers out of paying social security and other benefits due to direct hires and makes it easier to fire anyone who complains or supports unions., the LAP was supposed to end abusive subcontracting of those doing a company’s core work. When workers at Bucarelia learned about the promised reforms, and that the palm sector had been specifically identified in the LAP, they launched an organizing campaign, thinking they had a way forward.
Apr 4, 2014
 Thousands of Peruvians marched in Lima, the capital, yesterday in a strong show of support for an end to organized crime and related violence in Peru’s booming construction sector.
Thousands of Peruvians marched in Lima, the capital, yesterday in a strong show of support for an end to organized crime and related violence in Peru’s booming construction sector.
Unions and civil society leaders called for a systemic solution to the phenomenon of false “unions” that extort construction firms and turn building sites into battlefields across Peru. Violence related to worksite conflicts has resulted in the death of six construction worker union activists over the last three years and significant economic losses that affect construction projects, workers and their families.
Leaders of the march include the General Confederation of Workers of Peru (CGTP), the Construction Workers Federation, the Peruvian Human Rights Commission, the mayor of Lima, regional lawmakers and the Peruvian Chamber of Construction.

Mar 28, 2014
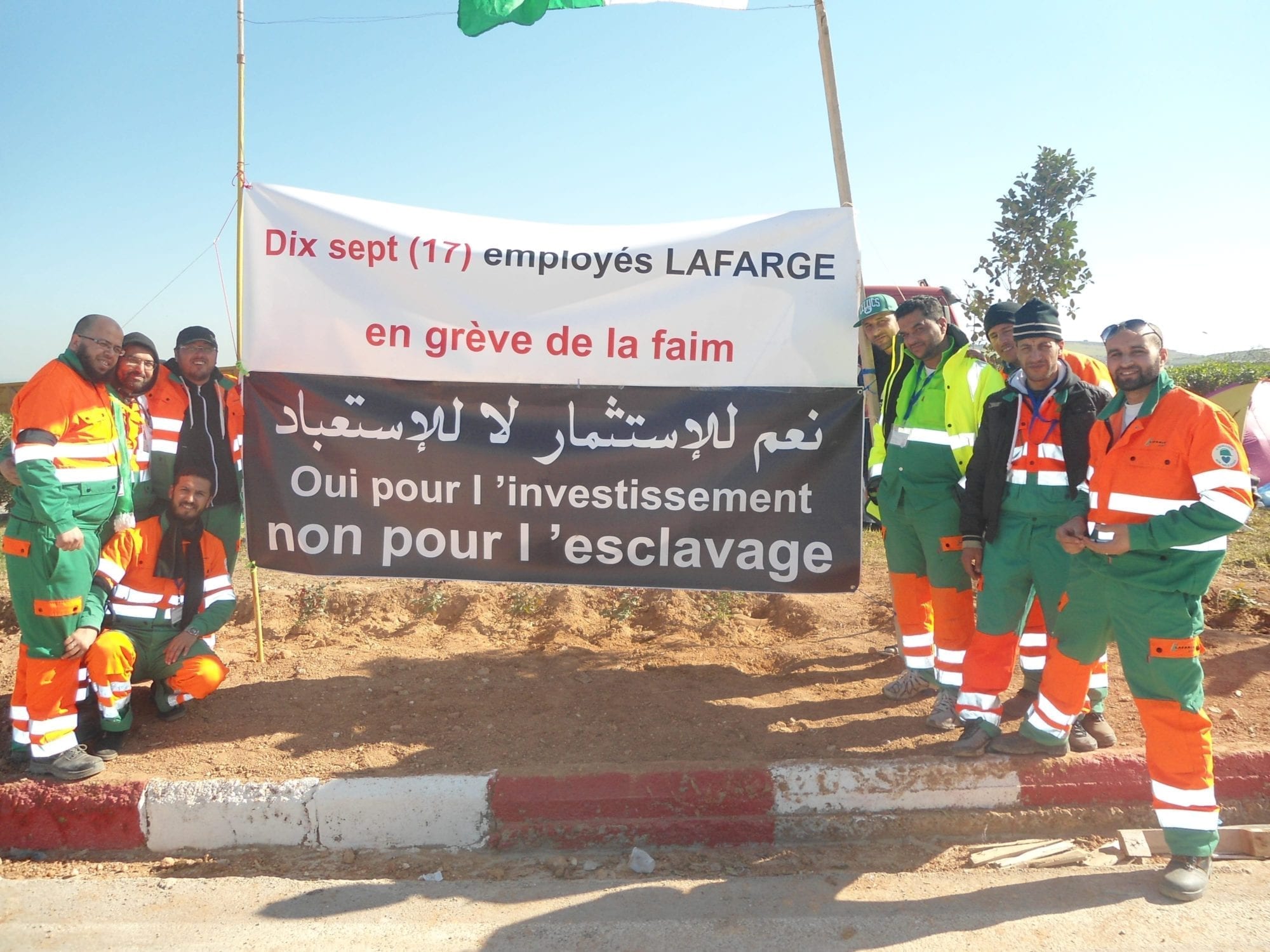
Seventeen workers who were suspended from their jobs in November 2013 at a cement plant in Oggaz, Algeria, have started a hunger strike to campaign for their rights.
In late 2013, the French Lafarge cement group took over the cement factory in Oggaz, in Western Algeria, and the company immediately set about restructuring and downsizing the operation. Workers attempted to resolve the matter through collective negotiation but were not successful. Then, despite record productivity, when the company unilaterally decided to reduce the bonus payments, the workers designated six workers to represent their grievances to management and staged a protest action. These six workers were immediately suspended. A collective work stoppage ensued, and company management retaliated by suspending an additional 11 workers.
The provisions of the cement workers collective agreement covering the application of the disciplinary process for suspended workers have been ignored. Despite repeated assurances, public authorities have so far refused to engage and resolve the matter.
The Lafarge cement workers reached out to the autonomous union SNAPAP for support, and their case has been documented by the Algerian press. On March 9, 2014, the 17 suspended workers started a hunger strike to bring attention to their illegal suspension and the gross violation of their human rights. “We are calling on the solidarity of workers everywhere and especially the global union federations IndustriALL and Building and Wood Workers International (BWI) to denounce both the silence and the indifference of the Algerian authorities in this matter” said Salim Mechri, a member of SNAPAP’s Executive Bureau.
Mar 27, 2014

Construction unions and migrant workers met this week in Costa Rica. Photo coursesy of BWI.
This week, eight construction union federation from six South and Central American countries came together in Costa Rica to focus on migrant workers and the issues they face in order to help migrants working in construction to organize and to improve union capacity to expand worker rights for migrant and native workers alike.
The seminar, jointly assembled by the Solidarity Center and Building and Woodworkers International (BWI), allowed union representatives the opportunity to present best practices for organizing migrant workers and to speak directly with Nicaraguan day laborers who also are active members of the Costa Rican BWI affiliate, SUNTRACS. Union leaders heard firsthand accounts of the daily challenges that Nicaraguan migrants face on the job and in Costa Rican society in general, where discrimination—including denial of treatment by the national health service for work-related injuries and receiving salaries that are below the national minimum wage—is a fact of life.
According to the International Labor Organization (ILO), more than 5 million people currently live and work in Latin American countries other than those in which they were born. Once a phenomenon almost exclusively restricted to developed countries in the Northern Hemisphere, positive trends in economic growth and job creation have converted numerous Latin American countries—such as Brazil, Chile, Argentina and Costa Rica—into attractive destinations for migrant workers over the last decade. Nonetheless, the promise of decent employment in these countries in sectors including construction, domestic work and agroindustry has remained elusive, particularly for workers without solid knowledge of their own labor rights enshrined by national law and international norms.
On a regional level, BWI and its affiliates have helped migrant workers obtain legal migratory status and advocated for more transparent national immigration policies. Most importantly, they have organized protest actions against insecure work environments, long working hours and wage irregularities for migrant workers.
BWI has seen positive results from its outreach efforts to migrant workers. “Objective economic conditions in Latin America have given new life to construction unions in the Southern Cone. The current construction boom in Brazil, for example, parallels what we saw in countries like the United States and Spain before the 2008 economic crisis,” said Nilton Freitas, BWI regional representative for Latin America and the Caribbean. “Using this new leverage and employing better forms of cooperation among our affiliates, we now are in a more advantageous position to prevent migrant workers from being treated as second-class citizens in the construction sector in those countries.”
The Solidarity Center and Building and Woodworkers International (BWI) have been working together over the last three years to promote innovative policies to improve union outreach and organization of migrant workers in the civil construction sector in Latin America. BWI’s pioneering role in the defense of immigrants who have sacrificed all to construct soccer stadiums in Brazil, skyscrapers in Singapore and offshore oil rigs in the Arabian Gulf was recently recognized by the AFL-CIO as the 2014 recipient of its prestigious George Meany-Lane Kirkland Human Rights Award.
Mar 25, 2014

Haitian migrant worker in the Dominican Republic. Credit: Solidarity Center.
This week the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights is meeting in Washington, D.C. One of the cases the commission will hear regards the Dominican Republic’s September 2014 Constitutional Court ruling that retroactively strips individuals who are unable to prove their parents’ regular migration status of their citizenship.
A new AFL-CIO and Solidarity Center report describes what this could mean for the people who will be disproportionately affected—individuals of Haitian descent living and working in the Dominican Republic, including those born in the country.
Those targeted by the court’s ruling will be excluded from any activity that requires official identification, including working in the formal sector, attending school, opening a bank account, paying into retirement or social security funds, accessing health services, getting married, traveling or voting. For many women, men and children born in the Dominican Republic, the ruling means being barred from participating in the only society they have ever known.
In the report, Dominicans of Haitian descent describe their struggle to maintain their status, pursue higher education, seek opportunities for meaningful work and career advancement, obtain justice against abusive employers and ensure their children are recognized as citizens and have access to critical services.
This deliberate creation of a stateless underclass is an egregious abuse of fundamental human rights and a clear violation of international law.
The AFL-CIO and Solidarity Center are committed to working with their union partners in the Dominican Republic, Haiti and overseas to ensure that all workers and their families in the Dominican Republic have full protection of their human and labor rights. The organizations call on the Dominican Republic to comply with its international obligations and ensure that Dominicans of foreign descent can fully and freely participate in society.
 The governments of Colombia and the United States signed the Labor Action Plan (LAP) three years ago this week. The plan was intended to provide a road map for Colombia to protect internationally recognized labor rights, prevent violence against labor leaders and prosecute the perpetrators of such violence.
The governments of Colombia and the United States signed the Labor Action Plan (LAP) three years ago this week. The plan was intended to provide a road map for Colombia to protect internationally recognized labor rights, prevent violence against labor leaders and prosecute the perpetrators of such violence.



